Advanced Spine Care by Expert Minimally Invasive Spine Surgeons
At D Spine Clinic, Mumbai’s leading spine care center, we specialize in minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS), offering cutting-edge solutions for a wide range of spine conditions. Led by Dr. Dhanish Mehendiratta, a top minimally invasive spine surgeon in Mumbai, our team delivers precise, patient-focused treatments designed for faster recovery, minimal scarring, and lasting results.
What is Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery?
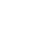
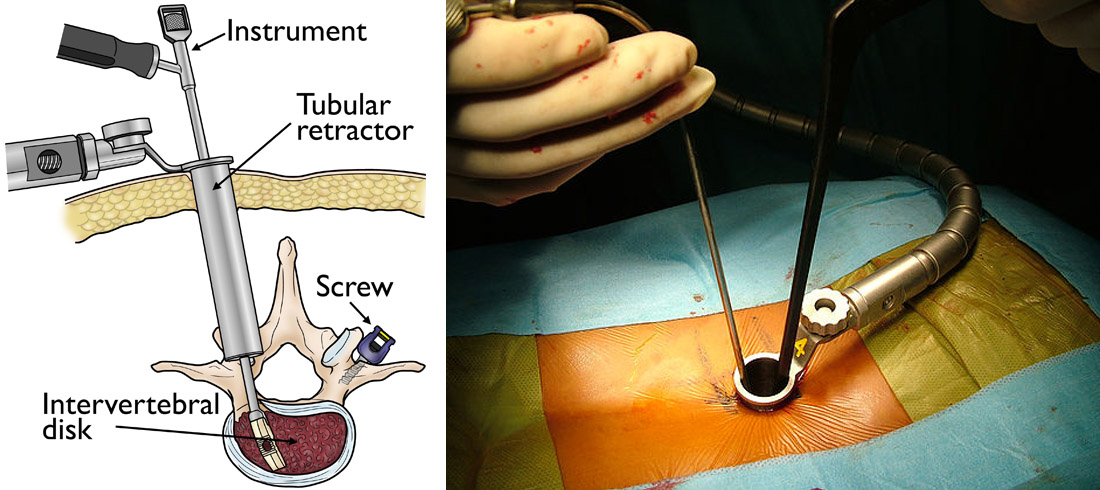
Minimally invasive spine surgery involves advanced techniques using small incisions, specialized instruments, and high-precision technology, such as microendoscopic tools and robotic assistance. Unlike traditional open surgery, MISS reduces tissue damage, blood loss, and recovery time, making it an ideal choice for patients seeking spine treatment in Mumbai.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery at D Spine Clinic
Choosing MISS at D Spine Clinic Mumbai offers distinct advantages:
- Smaller Incisions: Leading to less scarring and a better cosmetic outcome.
- Reduced Blood Loss: Less invasiveness translates to significantly less blood loss during surgery.
- Less Post-Operative Pain: Minimal muscle disruption means patients typically experience less pain after surgery, reducing the need for strong pain medications.
- Faster Recovery Time: Patients often have shorter hospital stays (sometimes even outpatient procedures) and can return to their daily activities, including work, much sooner than with traditional open surgery.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions inherently reduce the risk of surgical site infections.
Preservation of Muscle & Tissue: By avoiding extensive muscle cutting, MISS helps maintain spinal stability and function.
Conditions Treated with Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
At D Spine Clinic, our minimally invasive spine surgeons address a variety of spinal disorders, including:
- Herniated Discs: Microdiscectomy to relieve nerve compression.
- Spinal Stenosis: Decompression procedures to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
- Scoliosis: Corrective surgeries with minimal disruption.
- Spondylolisthesis: Stabilization using keyhole techniques.
- Spinal Trauma: Targeted interventions for fractures and injuries.
- Degenerative Spine Disorders: Fusion or decompression for chronic conditions.
Why Choose D Spine Clinic for MISS in Mumbai?
- Led by Dr. Dhanish Mehendiratta, a leading spine surgeon with international fellowships in robotic spine surgery and spinal deformity correction
- Advanced operation theater equipped for endoscopic and microscopic spine procedures
- Personalized treatment plans combining surgery, physiotherapy, and rehabilitation
- High patient satisfaction with excellent long-term outcomes
Start Your Journey to Pain-Free Living
If you’re suffering from back or neck pain, minimally invasive spine surgery at D Spine Clinic could be the solution. Contact us today to schedule a consultation with Dr. Dhanish Mehendiratta, Mumbai’s premier spine specialist, and discover personalized, advanced spine care in Mumbai.
A minimally invasive procedure is one that merely is less invasive than the alternative. The MISS goals are to give you the same outcome as an open surgery with less pain, fewer complications, and shorter recovery time. In some cases Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery can be performed via a surgical incision as small as one inch.
An open spinal surgery is one in which your surgeon makes an incision, or cut, typically about five to six inches long, and then moves the muscles to one side in order to operate on the bone.
Minimally invasive spine surgery, on the other hand, only requires a cut that’s about an inch long and uses a special tool called a retractor to spread push muscles out of the way. This causes far less trauma to your muscles, which means less post-surgical pain and a speedier recovery.
In addition to the shorter recovery times and improved function associated with MISS, other benefits include:
- Shorter hospital stays, with many procedures being performed on an outpatient basis using local anaesthesia instead of general anaesthesia.
- Reduced risk of infection
- Decreased post-surgical pain and narcotic use
- Less blood loss during surgery
- Less damage to soft tissue
- Reduced scarring
- Quicker return to activities of daily living (ADL), including work, self-care, and leisure
- Less post-operative rehabilitation
- Better postoperative quality of life
While your diagnosis alone can’t determine whether you’re a candidate for MIS, procedures that can commonly be performed using minimally invasive techniques include:
- Fusion
- Decompression
- Microdiscectomy
- Foraminotomy
- Laminectomy
- Laminotomy
- Kyphoplasty
- Vertebroplasty
MIS has grown more popular in recent years because patients tend to recover much faster and with less pain than with open surgeries.
A 2020 study found patients who underwent minimally invasive spinal fusions and decompressions resumed work and driving within 3 weeks of surgery. Meanwhile, open decompressions and fusions may require months of recovery.