Advanced Neuromonitoring in Spine Surgery by Expert Spine Surgeon in Mumbai
At D Spine Clinic, we utilize intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM)—a cutting-edge technology that enhances the safety and precision of spine surgeries. Under the expert guidance of Dr. Dhanish Mehendiratta, a globally trained spine surgeon in Mumbai, our team integrates real-time nerve monitoring to minimize surgical risks and protect spinal cord function during complex procedures.
This advanced approach ensures better outcomes, especially in surgeries involving delicate nerve structures or spinal deformities.
What Is Neuromonitoring in Spine Surgery?
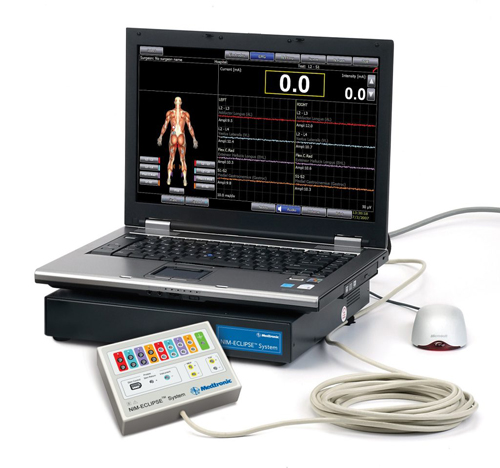
Neuromonitoring is a technique that provides real-time feedback on the functional integrity of the spinal cord and nerves during surgery. It uses specialized equipment to monitor electrical signals from sensory and motor pathways, helping surgeons avoid nerve damage and make informed decisions throughout the procedure.
At D Spine Clinic, we employ multiple neuromonitoring modalities, including:
- Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEPs) – Monitor sensory pathways
- Motor Evoked Potentials (MEPs) – Assess motor function and muscle response
- Electromyography (EMG) – Detect nerve root irritation or injury
Conditions Benefiting from Neuromonitoring in Spine Surgery
Neuromonitoring is particularly valuable for complex spinal procedures, including:
- Herniated Discs: Discs pressing on nerves, causing pain or weakness.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal leading to nerve compression.
- Scoliosis and Kyphosis: Spinal deformities requiring corrective surgery.
- Spondylolisthesis: Vertebral slippage causing instability or nerve irritation.
- Spinal Tumors or Cysts: Growths affecting spinal stability or nerve function.
- Degenerative Spine Conditions: Chronic conditions causing nerve compression or pain.
Neuromonitoring is especially recommended for:
- Spinal deformity corrections (e.g., scoliosis, kyphosis)
- Spinal tumor resections near critical nerves or spinal cord
- Complex disc surgeries in cervical or thoracic spine
- Spinal cord decompression in stenosis or trauma
- Revision spine surgeries where scar tissue may obscure anatomy
- Minimally invasive surgeries with limited direct visibility of nerves
- In all these cases, IONM enhances safety, especially when operating close to delicate nerve roots or the spinal cord.
Begin Your Customized Spine Treatment Plan
Your spine deserves the highest level of care. At D Spine Clinic, we combine surgical expertise with advanced neuromonitoring to ensure safe, effective outcomes. Schedule your consultation today and experience the future of spine surgery in Mumbai.
Neuromonitoring improves spine surgery safety by tracking nerve signals in real-time. It helps surgeons avoid nerve damage, adjust techniques instantly, and reduce the risk of complications like paralysis. It also leads to better outcomes and offers peace of mind to both patients and the surgical team.
It helps surgeons detect potential nerve or spinal cord issues immediately during the operation, reducing the risk of permanent neurological injury and improving surgical outcomes.
Electrodes are placed on the patient’s body to measure electrical activity in the nerves and muscles. These signals are monitored continuously by a specialist throughout the procedure.
Yes, it is non-invasive, safe, and widely used in spine surgeries to enhance patient safety and minimize the risk of complications.
A trained neurophysiologist or monitoring specialist works alongside the surgical team, interpreting the signals and alerting the surgeon to any changes that may indicate nerve stress or injury.